Workflow Overview
This document explains the process, roles, and permissions involved in creating and managing a Service inside a Domain in the Kadeck (DSH Preview) platform, following Data Mesh best practices.
Key Concepts
Service
- A Service consists of one or more applications (producers, consumers) operating in a single environment (e.g., Dev, QA, Prod).
- It includes related resources: topics, schemas, ACLs, consumer groups.
- A Service has Service Owners (users or groups) responsible for it.
Domain
- A Domain logically groups Services and topics.
- Domain Owners manage resources and ownership within a Domain.
Provisioning Profile
- A Provisioning Profile defines technical constraints for a specific environment within a domain.
- Topic configuration rules (e.g., max retention, replication bounds)
- Allowed schema types (e.g., Avro only)
- Permitted ACL actions
- Naming conventions for resources
- Created and managed by the Platform Team.
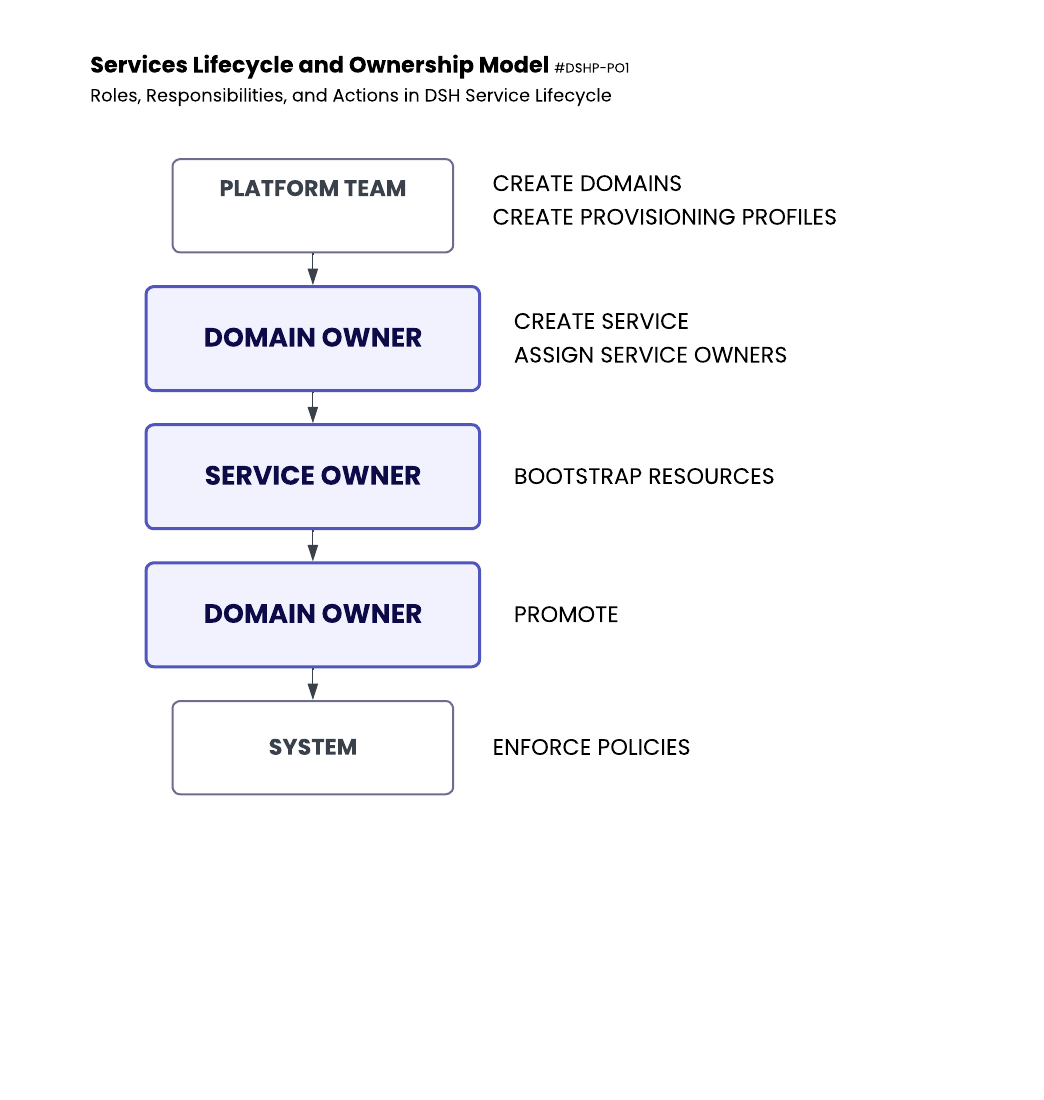
Roles
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Platform Team | Create Domains, Provisioning Profiles, set global policies |
| Domain Owner | Manage Domain, own services, promote services |
| Service Owner | Manage service resources within constraints |
| Data Steward | Review sensitive configurations if needed |
| Kadeck System | Enforce guardrails automatically |
Workflow Steps
1. Domain Setup
- Platform Team creates Domains and assigns initial Domain Owners.
- Platform Team defines Provisioning Profiles per environment.
2. Service Creation
- Domain Owner initiates new Service creation.
- Assigns Service Owners (individuals or groups).
- Service Name, Domain, and Environment are specified.
- Kadeck enforces guardrails based on Provisioning Profile.
Permissions:
- Only Domain Owners can create Services.
3. Resource Bootstrapping
- Service Owners bootstrap resources:
- Create topics, schemas, ACLs, consumer groups.
- Actions are constrained by:
- Provisioning Profile rules
- Service's namespace (naming conventions defined in provisioning profile)
- User's roles/groups (access control)
4. Resource Changes During Development
- Service Owners can reset topics, update schemas, adjust configs.
- Restricted to development environments unless otherwise allowed.
5. Promotion to Higher Environments
- Domain Owners promote services to higher environments (e.g., Dev → QA → Prod).
- Kadeck automatically enforces environment-specific Provisioning Profiles during promotion.
Permissions:
- Only users with Promotion Rights and who are Domain Owners can promote services.
6. Service Management
- Service Owners can manage runtime aspects.
- Domain Owners can change foundational configurations (e.g., service name, environment mappings).
- Changing a Service's Name requires Domain Owner action.
- Internal Service ID remains immutable for traceability.
7. Ownership Changes
- If Service Owners leave, Domain Owners can reassign ownership.
Key Rules
- Self-Service: Service Owners can act freely within guardrails.
- Platform Guardrails: Platform permissions and Provisioning Profiles always override.
- Domain Trust: Domain Owners have wide autonomy but critical changes are audited.
- Environment Isolation: Each environment holds its own Service instances.
- Direct Promotion: Moving to higher environments happens instantly if permissions allow.
Visual Flow